Highly Nonlinear Approximations for Sparse Signal Representation
Vector Space
A vector space over a field
![]() is
a set
is
a set ![]() together with two operations vector addition, denoted
together with two operations vector addition, denoted
![]() for
for
![]() and
scalar multiplication, denoted
and
scalar multiplication, denoted
![]() for
for
![]() and
and
![]() ,
such that the following axioms are satisfied:
,
such that the following axioms are satisfied:
-
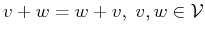 .
.
-
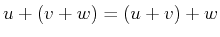 ,
,
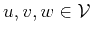 .
.
- There exists an element
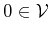 , called the zero vector, such that
, called the zero vector, such that
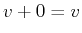 ,
,
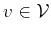 .
.
- There exists an element
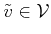 , called the
additive inverse of
, called the
additive inverse of 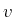 , such that
, such that
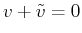 ,
,
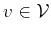 .
.
-
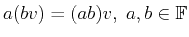 and
and
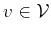 .
.
-
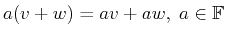 and
and
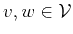 .
.
-
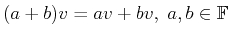 and
and
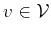 .
.
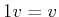 ,
,
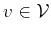 , where 1 denotes the multiplicative identity in
, where 1 denotes the multiplicative identity in
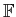 .
.

